Their Alphabet Started It All
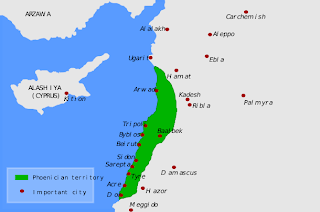
The Phoenicians were members of an ancient civilization based in the north of ancient Canaan, which approximates today’s modern Lebanon. Their civilization was a trading maritime culture that spread across the Mediterranean from 1550 BC to 300 BC, a period in history when there was no major military power in Mesopotamia, thus enabling smaller states like Phoenicia and the Hebrews to prosper. The term “Phoenicia” was actually from a Greek word that referred to the color of the dye from the snail murex ; the Phoenicians, however, referred to themselves as the “ Kena’ani ,” (or “Canaanites”), which incidentally is also a Hebrew word for “merchant.” Although the Phoenicians considered themselves a single nation, Phoenicia was not a unified state but a group of city-kingdoms, much like the ancient Greek city-states. The most important of these cities were Simyra, Zarephath (Sarafand), Byblos, Jubeil, Arw...


